. When Δ G is negative, a process will proceed spontaneously and is referred to as exergonic. The spontaneity of a process can depend on the temperature. Spontaneous processes In chemistry, a spontaneous processes is one that occurs without the addition of external energy.
Water Splitting Reaction at Polar Lithium Niobate Surfaces | ACS Omega
In order to determine whether a reaction is spontaneous (thermodynamically favourable) we use a physical quantity: Gibbs free energy Δ G \Delta G Δ G. When: Δ G < 0 \Delta G<0 Δ G < 0 – reaction is spontaneous. Δ G = 0 \Delta G=0 Δ G = 0 – reaction is at equilibrium. Δ G > 0 \Delta G>0 Δ G > 0 – reaction isn’t spontaneous

Source Image: pubs.acs.org
Download Image
I read somewhere that the difference between energetically favorable reactions and spontaneous reactions is that energetically favorable reactions are ones where energy is released, i.e., $\Delta H<0$, whereas spontaneous reactions are ones where the change in Gibbs free energy is negative, i.e., $\Delta G<0$. Thus it is possible for a reaction to be energetically favorable but not spontaneous

Source Image: sciencedirect.com
Download Image
Spontaneous Resolution of Chiral Janus-Type Double-Layered Metallocyclic Strips Incorporating Möbius Ring and Circular Helicate | Journal of the American Chemical Society Spontaneous Reactions. Reactions are favorable when they result in a decrease in enthalpy and an increase in entropy of the system. When both of these conditions are met, the reaction occurs naturally. A spontaneous reaction is a reaction that favors the formation of products at the conditions under which the reaction is occurring.

Source Image: pubs.acs.org
Download Image
Which Of The Reactions Are Spontaneous Favorable
Spontaneous Reactions. Reactions are favorable when they result in a decrease in enthalpy and an increase in entropy of the system. When both of these conditions are met, the reaction occurs naturally. A spontaneous reaction is a reaction that favors the formation of products at the conditions under which the reaction is occurring. The sign of ΔG depends on the signs of ΔH and ΔS. A reaction is spontaneous and favorable if there is a decrease in enthalpy and an increase in entropy of the system. In general, the conditions for a spontaneous reaction to occur are as follows: 1. When ΔG is negative, the reaction is spontaneous and proceeds in the forward direction. 2.
Redox-Driven Spontaneous Double Emulsion | ACS Macro Letters
Spontaneous reactions release free energy as they proceed. Recall that the determining factors for spontaneity of a reaction are the enthalpy and entropy changes that occur for the system. The free energy change of a reaction is a mathematical combination of the enthalpy change and the entropy change. (11.5.3) Δ G o = Δ H o − T Δ S o. Transformation of Supramolecular Membranes to Vesicles Driven by Spontaneous Gradual Deprotonation on Membrane Surfaces | Journal of the American Chemical Society

Source Image: pubs.acs.org
Download Image
Molecules | Free Full-Text | Comparsion of Catalyst Effectiveness in Different Chemical Depolymerization Methods of Poly(ethylene terephthalate) Spontaneous reactions release free energy as they proceed. Recall that the determining factors for spontaneity of a reaction are the enthalpy and entropy changes that occur for the system. The free energy change of a reaction is a mathematical combination of the enthalpy change and the entropy change. (11.5.3) Δ G o = Δ H o − T Δ S o.
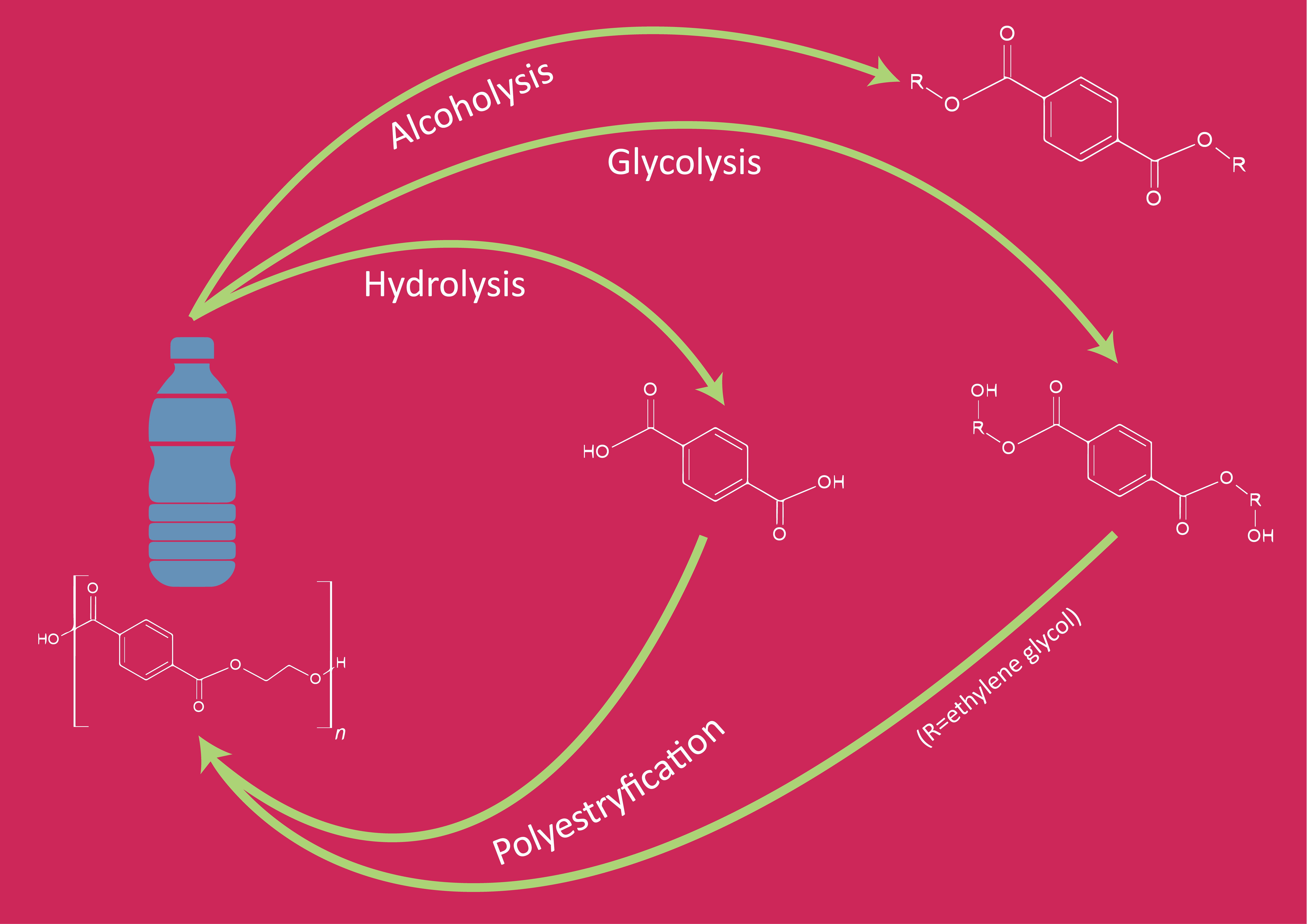
Source Image: mdpi.com
Download Image
Water Splitting Reaction at Polar Lithium Niobate Surfaces | ACS Omega . When Δ G is negative, a process will proceed spontaneously and is referred to as exergonic. The spontaneity of a process can depend on the temperature. Spontaneous processes In chemistry, a spontaneous processes is one that occurs without the addition of external energy.

Source Image: pubs.acs.org
Download Image
Spontaneous Resolution of Chiral Janus-Type Double-Layered Metallocyclic Strips Incorporating Möbius Ring and Circular Helicate | Journal of the American Chemical Society I read somewhere that the difference between energetically favorable reactions and spontaneous reactions is that energetically favorable reactions are ones where energy is released, i.e., $\Delta H<0$, whereas spontaneous reactions are ones where the change in Gibbs free energy is negative, i.e., $\Delta G<0$. Thus it is possible for a reaction to be energetically favorable but not spontaneous

Source Image: pubs.acs.org
Download Image
Production of Reactive Oxygen Species by the Reaction of Periodate and Hydroxylamine for Rapid Removal of Organic Pollutants and Waterborne Bacteria | Environmental Science & Technology Step 1 1 of 4 In this exercise we need to determine which of the following reactions are spontaneous (favorable). Step 2 2 of 4 A spontaneous reaction is a reaction that is thermodynamically favourable and will proceed without an extra input of energy.

Source Image: pubs.acs.org
Download Image
Real Spontaneous Combustion – Cairncrest Farm Spontaneous Reactions. Reactions are favorable when they result in a decrease in enthalpy and an increase in entropy of the system. When both of these conditions are met, the reaction occurs naturally. A spontaneous reaction is a reaction that favors the formation of products at the conditions under which the reaction is occurring.

Source Image: cairncrestfarm.com
Download Image
KWOK The Chem Teacher: Chemical Energetics – Applying Gibbs Free Energy The sign of ΔG depends on the signs of ΔH and ΔS. A reaction is spontaneous and favorable if there is a decrease in enthalpy and an increase in entropy of the system. In general, the conditions for a spontaneous reaction to occur are as follows: 1. When ΔG is negative, the reaction is spontaneous and proceeds in the forward direction. 2.
Source Image: kwokthechemteacher.blogspot.com
Download Image
Molecules | Free Full-Text | Comparsion of Catalyst Effectiveness in Different Chemical Depolymerization Methods of Poly(ethylene terephthalate)
KWOK The Chem Teacher: Chemical Energetics – Applying Gibbs Free Energy In order to determine whether a reaction is spontaneous (thermodynamically favourable) we use a physical quantity: Gibbs free energy Δ G \Delta G Δ G. When: Δ G < 0 \Delta G<0 Δ G < 0 – reaction is spontaneous. Δ G = 0 \Delta G=0 Δ G = 0 – reaction is at equilibrium. Δ G > 0 \Delta G>0 Δ G > 0 – reaction isn’t spontaneous
Spontaneous Resolution of Chiral Janus-Type Double-Layered Metallocyclic Strips Incorporating Möbius Ring and Circular Helicate | Journal of the American Chemical Society Real Spontaneous Combustion – Cairncrest Farm Step 1 1 of 4 In this exercise we need to determine which of the following reactions are spontaneous (favorable). Step 2 2 of 4 A spontaneous reaction is a reaction that is thermodynamically favourable and will proceed without an extra input of energy.